Rubber is defined as a material that has elastic properties. So that its most important property is stretching, so that sometimes it stretches up to 60 % of its original length. Natural rubber loses heat when stretched and absorbs heat when returned. In general, rubber is a material that has low elasticity and high shrinkage. The term polymer is used to describe rubber in its raw state. One of the advantages of rubber, especially synthetic rubber, is that by increasing or decreasing its composition, the desired properties can be achieved. The rubber is not perishable and does not normally need lubrication. Its hardness increases over time so that after vulcanizing the rubber (combining with sulfur) after a few hours at normal temperature, its hardness increases sharply.
In general, the import of rubber parts is mostly in the field of tires, tubes, transmission belts (of any type), impeller belts, industrial conveyor belts (conveyor belts), fire hoses. At present, many types of rubber are produced using both natural rubber and synthetic rubber, which are mostly used in car factories, and thus a large volume of production of rubber factories and workshops is made up of car parts. The production process of rubbers is one of the major manufacturing industries. The production of this product has special complexities and is done in large production halls.
Types of Rubbers:
rubbers are usually available in two types bias and radial. In the production of bias rubbers, older technology is used, in which cotton fibers are used to produce rubbers. While for the production of radial rubbers, wire strands are used. Bias rubbers have disadvantages compared to radial, including a reduction in the life of the bias rubbers and their adhesion to the road, due to the deformation of the contact surface of the tread. In contrast, radial rubbers have a strong structure due to the use of wire strands in their structure and their tread shape changes less, so in the corners, they have good adhesion to the road surface. Another advantage of radial rubbers is their higher speed tolerance than bias rubbers, and the life of these rubbers is 40 to 60% longer than bias rubbers.

Rubbers Production Line:
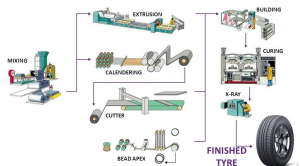
First Stage:
The first step in the production of rubbers is to produce a rubber compound. In this section, raw materials are mixed together in a blender (Banbury Mixer) and various rubber compounds are obtained, including rubber (natural and synthetic), rubber additives, soot, oils, and chemicals. Rubber compounds are used in different parts of rubber. And since each tire has different physical and mechanical properties, it is necessary to prepare different combinations of rubber materials. Soot, which has anti-wear properties in rubber and fills intermolecular cavities. Antioxidants help increase the life and strength of the part in this cycle. Oil is used as an emollient.
Blending is a step in which obtaining the best formulation to combine several different types of materials with the selected rubber, to achieve parameters such as desired properties, better and easier vulcanization, a more suitable forming method, and reach a more reasonable price. These materials are mixed with rubber and the rubber compound is ready for processing.
Second Stage:
The rubber is placed in the process of mixing with raw materials, and after complete mixing, it enters the second stage, which is called rubber curing, and the desired part, under certain pressure and temperature, is baked by press machines. This stage when sulfur is added as a rubber curing agent is called vulcanization. Due to the time curing process, some alternative ingredients are used to speed up curing. Sulfur compounds, zinc oxide, stearic acid, and antioxidants. The addition of these materials creates a good adhesion to the rubber and the right combination of ingredients. After leaving the mixing and cooling stage, the compound turns into a sheet.
Forming:
Forming means the gradual formation of a rubber compound. It should be said that the forming machines in tires are almost similar to the forming machines in plastics. The choice of a shaping process should be made taking into account the technical and economic parameters as well as to achieve completely uniform curing in the product. There are several methods for molding rubber parts that can be divided into three general categories, compression molding, injection molding, and transfer molding. Other molding methods can be considered as a combination of these three methods.
Compression Molding:
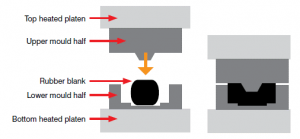
Compression molding is a type of forming method in which the rubber material is placed exactly in the metal mold and then softened by heat and then compressed to have a shape according to the mold.
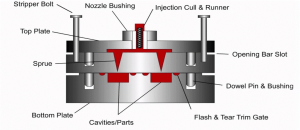
Injection Molding:
Injection molding in rubber parts is very similar to plastic parts, and in this method, raw rubber is injected into the mold at high temperatures and pressure. The use of this method in mass production is very common due to the high speed of production, however, this method of molding has many weaknesses compared to the other two methods, the most important of which is the expensive equipment used in this method. It is also not possible to use all types of rubber in this process and the rubber used must have a very low viscosity, so the rubber parts produced in this way usually do not have acceptable mechanical properties compared to the other two methods.
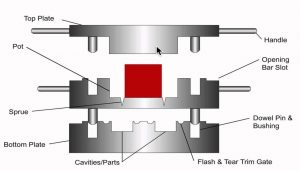
Transfer Molding:
transfer molding can be considered the most strategic method of production of rubber parts, parts with large dimensions and special geometric shapes can be produced in this way without any restrictions on the polymer base in terms of physical and chemical properties. Of course, this method of molding is very difficult and time-consuming and is only used in limited production and special parts that cannot be produced by other methods. To produce with this method, many parameters must be checked and controlled, for example, the temperature of the mold before the injection operation must be lower than the curing temperature of the rubber and also conditions must be predicted that after the injection phase, the mold quickly reaches the curing temperature.
the temperature in different parts of the mold should be the same and controllable, and the production schedule should be such that the curing is done completely and no trace of burn or immaturity is observed in the part.
Third stage:
Finally, the produced tires are tested according to certain standards. The outer and inner parts of the produced tire are examined and in the next steps are evaluated with test devices and then with laser beams in the X-Ray machine, images of rubber parts are taken in terms of air bubbles and separation between the tire components.






