Description
Diethylenetriamine (DETA) also known as 2,2’-Iminodi(ethylamine) is an organic compound with the formula HN(CH2CH2NH2)2. It is a weak base and its aqueous solution is alkaline. DETA is a byproduct of the production of ethylenediamine from ethylene dichloride. Shanghai Chemex is one of the most reputable suppliers of this chemical in the world.
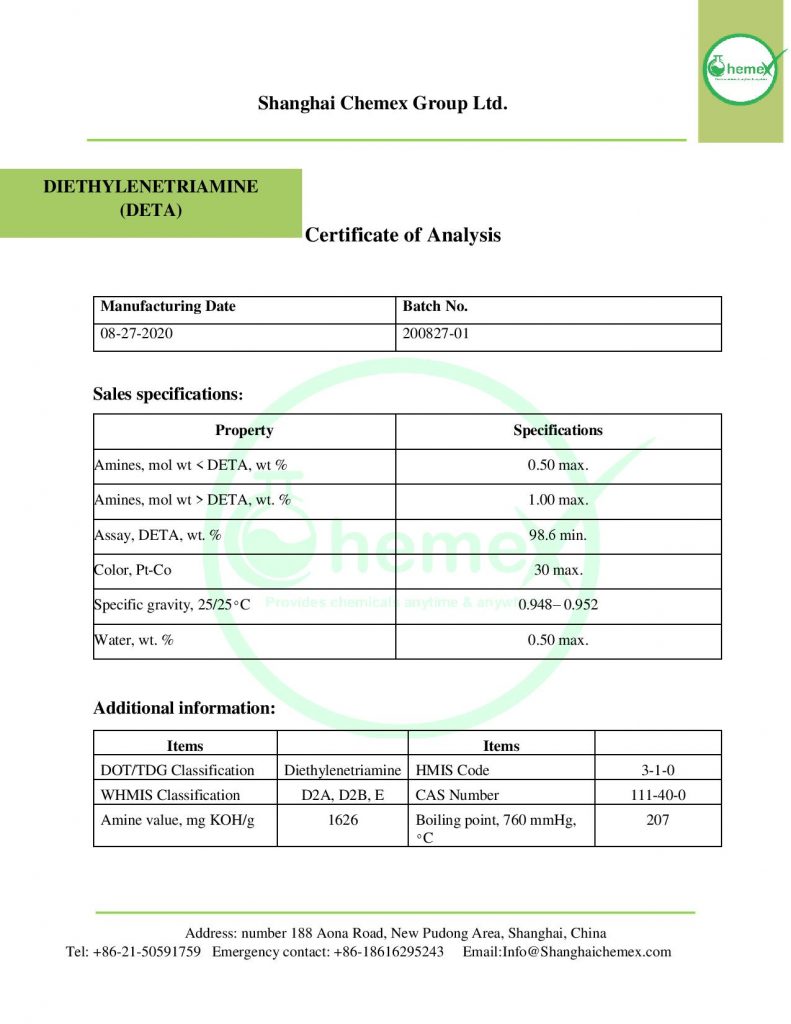
Physical and Chemical Properties:
| Chemical formula | C4H13N3 |
| Molar mass(g/mol) | 103.169 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Ammoniacal |
| Density(mg/ml) | 955 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point(° C) | −39.00 |
| Boiling point(° C) | 204.1 |
| Solubility in water | miscible |
Diethylenetriamine Production Process:
this method relates to a cyclic two-step process for the production of diethylenetriamine from ethylenediamine, monoethanolamine, and urea.
It is known that diethylenetriamine can be made by the reaction of ethylene dichloride with excess ammonia, followed by caustic hydrolysis of the amine hydrochloride salt thereby formed. A homologous mixture of ethylene amines results from this process, ranging from ethylenediamine to pentaethylenehexamine. Product selectivity is controlled mainly by varying the ethylene dichloride to ammonia ratio. A selectivity to ethylenediamine of about ninety percent can be achieved by a proper choice of this ratio, but selectivity to diethylenetriamine or higher homolog is poor. However, a method for preparing diethylenetriamine with a high degree of selectivity in high yields with little or no nonuseable by-products being formed is not known.
this process comprises the steps of (a) reacting ethylenediamine, ethanolamine, and urea in an inert atmosphere to form amino ethylethyleneurea, ethylene urea, and ammonia; and (b) hydrolyzing the amino ethylethyleneurea and ethylene urea formed in step (a), in an inert atmosphere and in the presence of a Bronsted base catalyst, to form diethylenetriamine and ethylenediamine.
Diethylenetriamine Uses:
|
|






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.