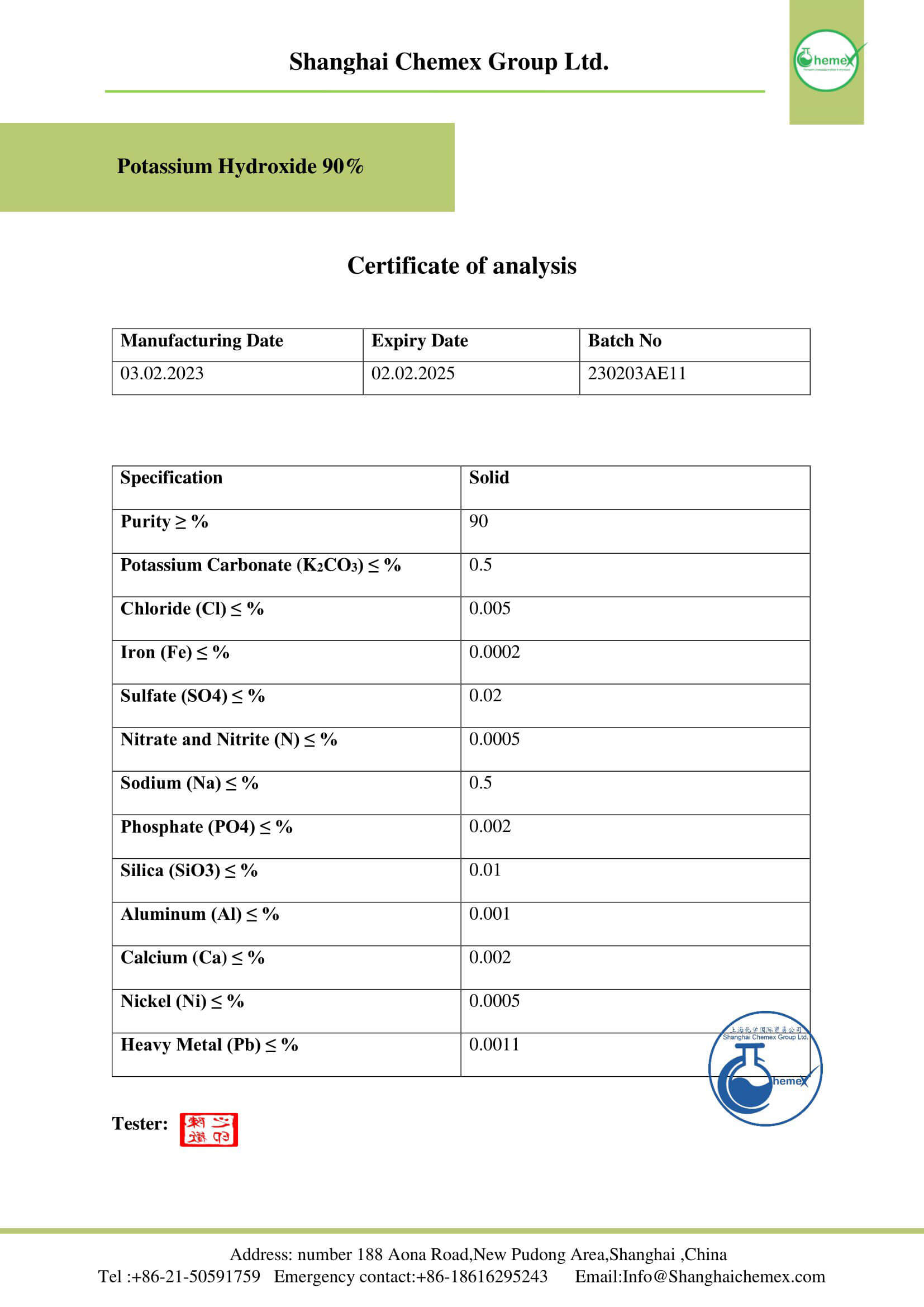
Description
Potassium hydroxide is a mineral compound with the formula KOH, more commonly known as potash. Potash, along with sodium hydroxide or caustic soda (NaOH), is one of the strongest bases. This compound has many industrial uses, most of which are based on its combustion and reaction properties with acids. Shanghai Chemex is one of the most reputable manufacturers of this chemical in the world.

Physical and Chemical Properties:
Potassium hydroxide is usually sold in the form of clear-colored pellets whose surface becomes sticky when exposed to air; Because potash has hygroscopic properties; That is, it absorbs water molecules from the space around it. In addition, commercial samples of potassium hydroxide usually contain varying amounts of impurities consisting of water and carbonates; The physical and chemical properties of this material can be summarized in the table below:
| Chemical formula | KOH |
| Molecular Weight(g/mol) | 56.11 |
| Appearance | solid |
| odor | odorless |
| Density (g/mL at 25 °C) | 2.12 |
| PH (aqueous solution) | Strongly alkaline |
| Melting point (° C) | 360 |
| Boiling point (° C) | 1,327 |
| Water Solubility (g/100 mL at 25 °C) | 121 |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, glycerol
insoluble in ether, liquid ammonia |
| color | White or colorless |
| form | pieces, lumps, or sticks having a crystalline fracture |
| Other names | Caustic potash, Lye, Potash lye, Potassium hydrate, KOH |
| Chemical Structure Depiction | 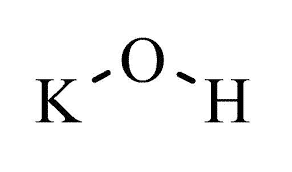 |
The Production Process of Potassium Hydroxide:
In the old method, potassium hydroxide was synthesized by adding potassium carbonate to a strong solution of calcium hydroxide (lime). In this method, the formed calcium carbonate is filtered and the remaining solution is boiled to obtain potash.
Ca (OH)2 + K2CO3 → CaCO3 + 2 KOH
The current method for the synthesis of potassium hydroxide is the electrolysis of potassium chloride solution, which is similar to the production of sodium hydroxide. In this method, hydrogen gas and chlorine gas are by-products.
2 KCl + 2 H2O → 2 KOH + Cl2 + H2
Potassium Hydroxide Uses:
- Potassium hydroxide is used in the manufacture of a variety of ingredients, including liquid soaps, lotions, shampoos, and hair sprays. While the use of sodium hydroxide is more common in soap, potassium hydroxide soaps are more soluble in water and less hazardous to the environment.

- Potash is used in industrial compounds such as stove cleaners, road cleaners, and in nonphosphate detergents, pipes, and drain cleaners.
- The alkaline solution of potash provides high ionic conductivity for the battery and therefore makes alkaline batteries cheaper and better in terms of performance than carbon batteries.
- Potassium hydroxide is often used as a food additive in commercially processed foods or as a chemical coating for fruits and vegetables. It is added to processed foods as a stabilizer for longer shelf life and as a thickener.
Why Potassium Hydroxide is used in Agriculture?
Potassium hydroxide is used in agriculture to produce fertilizer and supply the required potassium in the soil. Considering that potassium is one of the main substances for optimal growth and photosynthesis in plants, its use in fertilizers to supply potassium is of special importance. Since some plants are sensitive to chloride ions, the use of fertilizers containing potassium hydroxide is very effective for this type of plant. Other uses of this substance in agriculture include its use in herbicides and fungi. To prevent pests, the combination of a phosphorus acid with potassium hydroxide is regularly sprayed on plants. The presence of potash also helps regulate the pH of acidic soils.

Buy Potash:
Contact our experts at Shanghai Chemex to buy potash and also to know the price, analysis, and order registration.
Safety Information:
Contact with potassium hydroxide due to its high alkaline power can penetrate the skin and tissues of the body. Contact of skin and eyes with this compound can cause burns, severe irritation, and even blindness. Inhalation can damage the mucous membranes and lungs and, if swallowed, can be very toxic and lead to permanent tissue damage or even death.
This material is not flammable, but in case of contact with metals, especially when wet, it causes corrosion and the release of hydrogen gas, and there is a possibility of explosion in these conditions.
Packing and Storage:
Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible substances, strong acids, water, metals, and flammable liquids.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.