When it comes to a proper detergent, it means that a solution has been prepared that can remove contaminants of any physical or chemical nature from the surface. The first man-made detergent is soap, which has been around for centuries. With the passing of time and the advancement of technology, a wide range of detergent products with powerful cleaning properties were produced and entered the market. What makes the use of a detergent even more prominent is its power in cleaning surfaces. These surfaces can include metal and plastic surfaces, wood surfaces, fiberglass or alloys, silver gold, and the like. In the continuation of this discussion, we will get acquainted with the types of categories for detergent solutions and their uses.
What are the Chemicals used in the Detergent Industry?
Alkalines:
Alkalis, which are the main constituents of most detergents, are actually soluble and alkaline salts that react with a neutral acid to neutralize it. These compounds are effective in removing contamination and fabric stains without excessive wear.
Catalyst Enzymes:
Enzymes are divided into natural and chemical categories. Different enzymes have different properties and perform different catalytic actions to eventually break down large molecules into smaller molecules. The extraction of enzymes from nature and their application in the detergent industry dramatically transformed this industry. Enzymes allow us to have cleaner clothes with lower water temperatures and less detergent.
- Protease: Cleans protein-based contaminants
- Amylase: removes contaminants based on starch or carbohydrates
- Cellulase: breaks down cotton fibers
- Lipase: Cleanses fat-based contamination
- Pectinase: removes fruit-based stains
Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS):
Sodium lauryl sulfate is an organic and synthetic compound known as a (surfactant) and reduces the surface tension between materials, so it is used as a cleanser and foaming agent. SLS is derived from a mixture of palm and coconut oil.
Sodium lauryl Ether Sulfate:
It is an anionic detergent and surfactant found in many care products (soaps, shampoos, toothpaste, etc.).
Sodium Polyphosphate:
Sodium polyphosphate with the chemical formula (NaPO3) n, also known as polyphosphate, is one of the most widely used materials in the detergent industry. Phosphates are used in dishwasher and washing machine powders to soften water and are effective in removing dust and grease.
Sodium Tripolyphosphate:
Sodium tripolyphosphate improves the ability of various detergent elements to penetrate deeper into the fibers of clothing and creates foam.
Sulfonic Acid:
Sulfonic acid is one of the most important compounds of organic sulfur and is widely used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. Salts and other alkaline derivatives are used in detergents, paints, and water-soluble catalysts.
Betaine:
Betaine is a natural substance that is used to increase the concentration and improve the texture of some products. It also helps hydrate the skin and hair.
Lauramide:
Lauramide with the chemical formula C4H11NO2 is a di ethanolamide made from a mixture of fatty acids of coconut oil and di ethanolamide. It is a non-ionic surfactant that acts as a foaming and thickening agent and acts as an emulsifier in detergents such as shampoos and hand soaps and other care products.
Glycerin:
Glycerin is added to all types of soaps as emollients and tonics, especially moisturizing soaps or special soaps for the face.
Types of Industrial Detergents based on Electric Charge:
Industrial detergents are classified as follows according to the electric charge they carry:
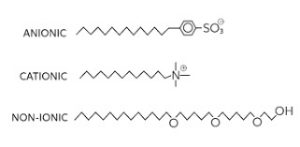
Anionic Detergents:
A surfactant or detergent that has a negative charge is called anionic detergent. Common cleaners are alkylbenzene sulfonates. In anionic detergents, the alkylbenzene moiety of these anions is lipophilic and hydrophobic, and the sulfonate moiety is hydrophilic. Two different types of these anionic detergents are common, those with branched alkyl groups and those with linear alkyl groups.
Cationic Detergents:
Cationic detergents have a pure positive electric charge. The chemical structures of cationic detergents are similar to those of anionic detergents, but the sulfonate group is replaced by quaternary ammonium.
Non-ionic Detergents:
Non-ionic detergents contain a hydrophilic group without charge. These compounds are usually based on glycosides (sugar alcohol) or polyoxyethylene.
Preparation of Detergents:
- In the manufacture of detergents and chemicals, observing the degree of quality and purity of raw materials is of great importance if this issue is not observed, the desired result will not be achieved.
- Choosing the right temperature for different chemical compounds is of particular importance.
- Sample tests should always be performed in low amounts, both to avoid large losses and to repeat the experiment to achieve the desired result at a lower cost.
- In most cases, if the raw material is not available or a high cost is required to produce it, small changes can be made in terms of weight, temperature, replacement of the raw material, or even production of the same raw material to achieve similar results and even in some Sometimes he got better results.
The General Formula of Detergent:
Detergents are defined as ammonium or alkyl benzene sulfonate, which are salts of a long chain of carboxylic acids with the chemical formula C18H29NaO3S.
Properties of Suitable Detergent:
Suitable types of industrial detergents, regardless of their type, have some distinguishing characteristics. These features are one of the most important factors in choosing the right detergent for the cleaning process of various surfaces and contaminants. The most important of these specifications are:
- High ability to remove water hardness
- Perfectly soluble in water
- Non-corrosive
- Non-toxic and environmentally friendly
- Economically viable
- High wetting and penetrating ability
- Degreasing ability
- Proper drainage capability
- Ability to remove rust and shells
Examples of Types of Detergent:
Soap:
Soap is a sodium or potassium salt of fatty acids that is used to remove grease and dirt. Soap is the first man-made detergent and is now available in solid and liquid forms. Glycerin, coconut oil, and sorbitol are emollient compounds in soap. Tetrasodium etidronate is another substance that is used to protect the color and fragrance, and EDTA-2Na and EDTA-4 Na is the main detergent used in the composition of various soaps.
Soap Liquid:
If a lot of coconut oil or oils like linseed oil are used in a normal building, we can liquefy the soap. Liquid soaps, in addition to the raw material of liquid soap production, contain other substances such as emollients, cleansers and foams, antibacterials, and lubricants.
Powder:
These detergents are produced in such a way that they do not damage clothes and fabrics. Dimethyl ammonium chloride (cationic surfactants) and derivatives of polyoxyethylene, polyoxypropylene, alkanol amides (anionic surfactants), and coco amido propyl betaine (amphoteric surfactants) are used in washing powder. Washing powder contains a bleaching agent called perborate, which is not found in hand powder. Trisodium phosphate is another surfactant that removes pus and fat. Acetylene diamine is the most widely used stain and bleach compound in these detergents.
Shampoo:
Shampoos are common detergents that everyone uses and are composed of water, surfactants, foams, and additives. The chemicals in shampoo formulations are designed to remove grease and dirt from the hair and scalp, so they are not very strong. Sodium lauryl ether sulfate and disodium lauryl sulfosuccinate are anionic surfactants in the shampoo with foaming power. Cocamidopropyl betaine, diethanolamine, polysorbate, and polyethylene glycol distearate are mild amphoteric surfactants used in shampoos. Citric acid is also used in some anti-dandruff shampoos.
Degreasers:
These detergents contain Sodium hydroxide and Potassium hydroxide, which react with fats and hydrolyze them. Another ingredient in these detergents is ammonia, and in addition alkaline compounds, silicates and phosphates are usually added to their formulations.
By this article, it can be concluded that detergents are currently one of the most essential materials needed to maintain health, and without them, life would not be possible due to the existing pollution. Nowadays, even detergents are used in various industries to remove grease and oil from parts and devices, and they have really become an integral part of our lives.










2 Responses
What is the main ingredient in laundry detergent?
The most common materials are ammonium, potassium, or sodium salts of toluene, xylene, or cumene sulfonates.